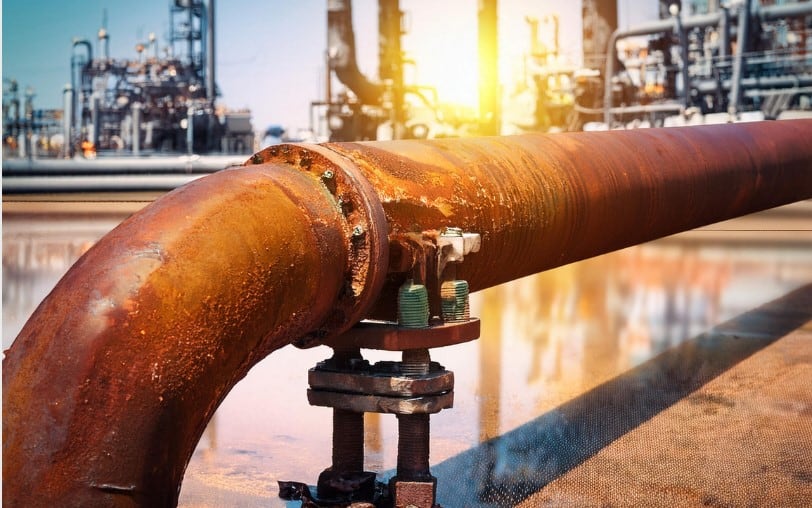
In corrosive environments such as chemical processing plants, oil refineries, and offshore platforms, preventing leaks is one of the primary concerns for maintaining the integrity of industrial piping systems. Aggressive chemicals, saltwater, and severe weather conditions accelerate the corrosion of metal components, leading to pipe degradation, support failure, and eventually, leaks. These environments demand the use of advanced materials and systems that can resist corrosion over time.
While traditional metallic pipe supports have long been used due to their strength and durability, they are highly vulnerable to corrosion. Over time, the metal’s integrity deteriorates, leading to leaks and costly repairs. One of the most effective solutions to combat corrosion-related issues is the adoption of composite supports. These supports, such as those offered by RedLineIPS, are made from corrosion resistant materials like fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP), significantly enhancing the lifespan of the piping infrastructure.
Understanding Corrosion in Industrial Piping Systems
Types of Corrosion Affecting Piping Systems
- Uniform Corrosion: This occurs evenly across a metal surface, often as a result of exposure to a uniform corrosive environment. Although predictable, uniform corrosion can still cause extensive metal loss over time.
- Pitting Corrosion: A localized type of corrosion that results in small pits or holes on the metal surface. These pits can penetrate deep into the material, leading to sudden leaks or failure. Pitting corrosion is particularly dangerous because it is difficult to detect until significant damage has already occurred.
- Crevice Corrosion: Occurs in confined spaces, such as under gaskets or pipe supports. In these areas, stagnant corrosive environments form, leading to rapid degradation. Crevice corrosion is difficult to spot and can cause severe localized damage in a short period.
- Galvanic Corrosion: Happens when two dissimilar metals are in electrical contact in the presence of an electrolyte, such as saltwater. The more anodic metal corrodes faster, accelerating material degradation.
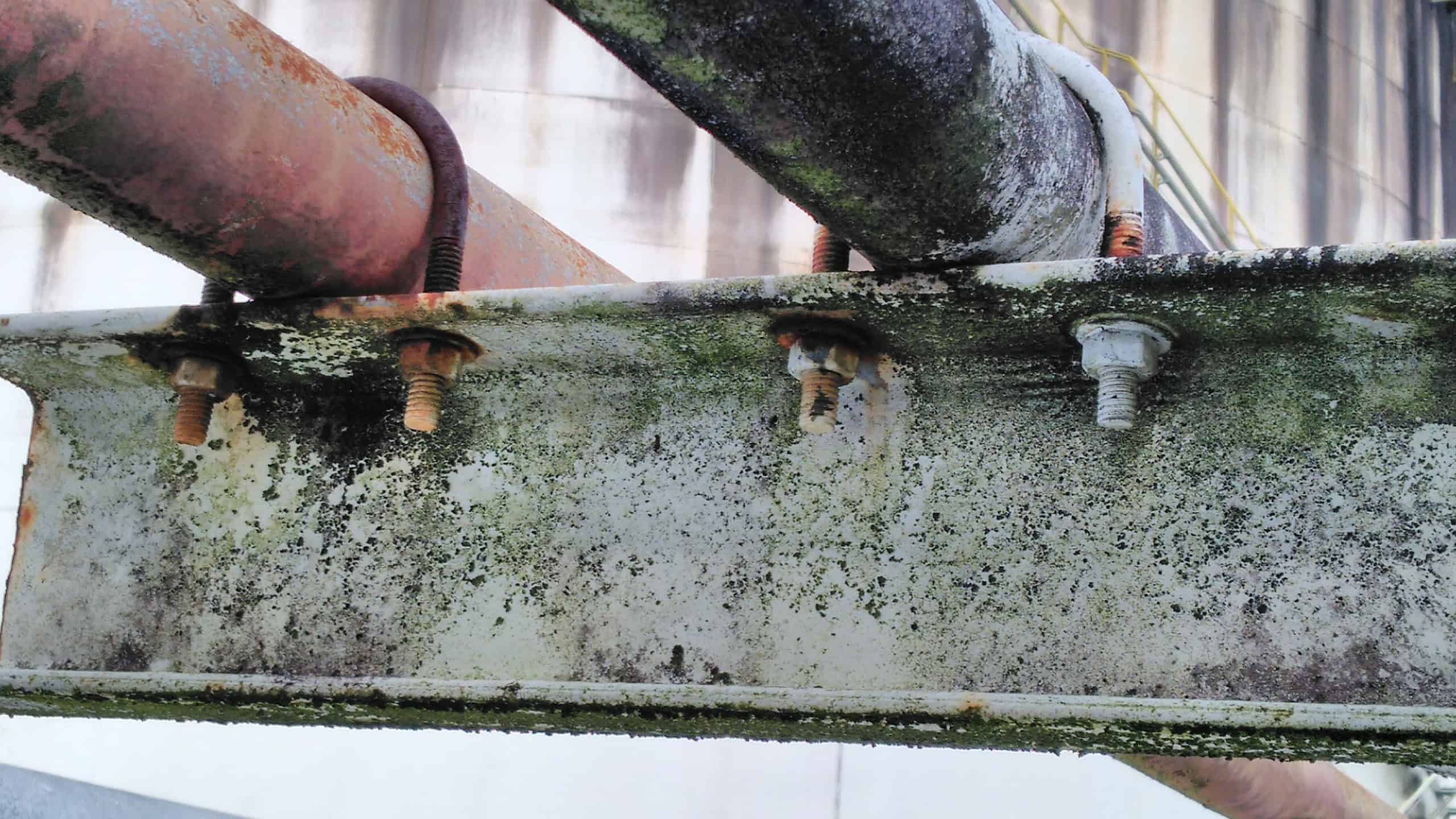
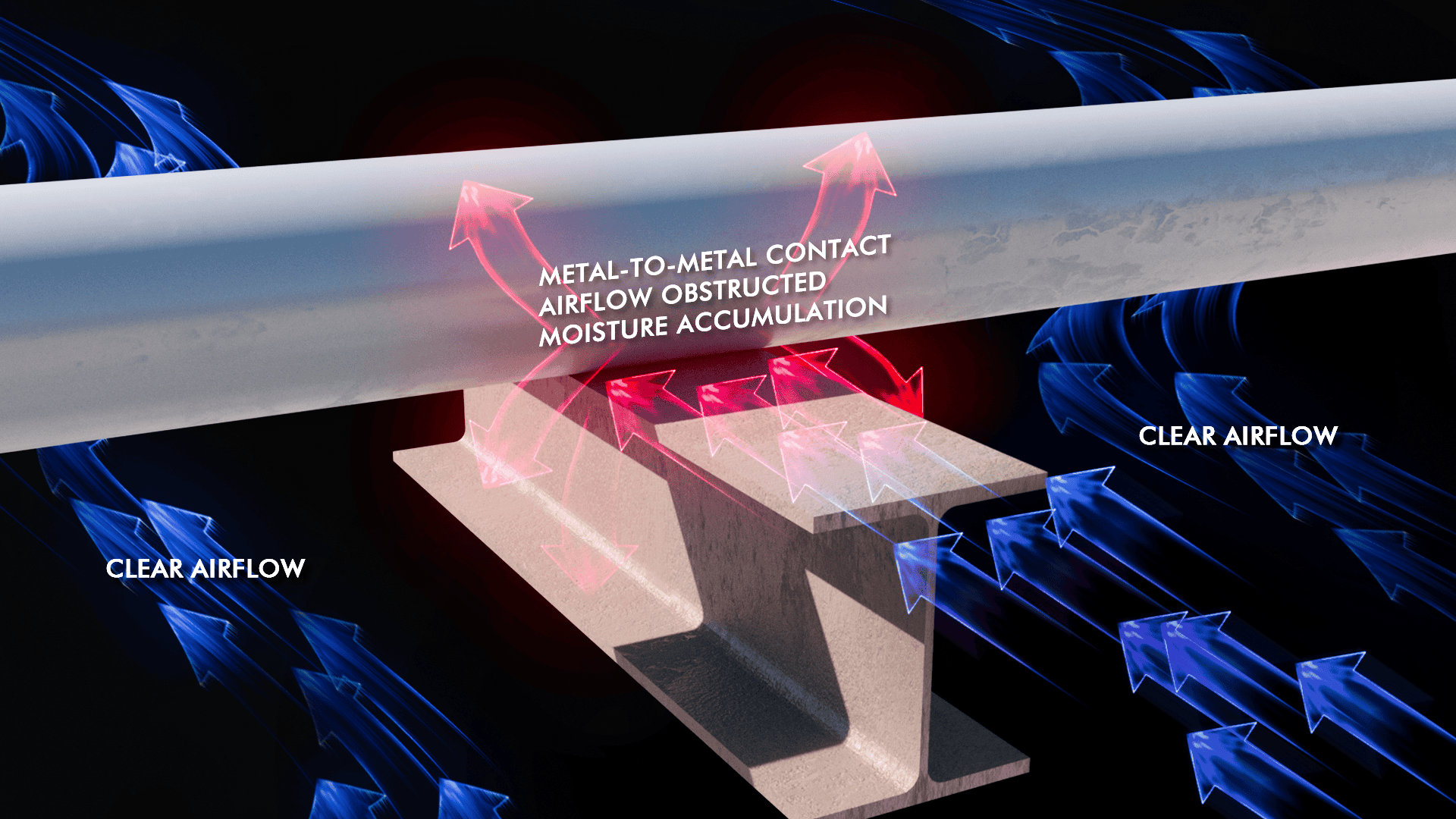
CUPS (Corrosion Under Pipe Supports)
A major contributor to leaks in industrial piping systems is Corrosion Under Pipe Supports (CUPS). This type of corrosion occurs at the interface between the pipe and its support, typically in crevices where water or corrosive chemicals can accumulate. The limited ventilation in these areas allows moisture to remain trapped, creating a microenvironment perfect for corrosion to thrive.
Over time, CUPS weakens the pipe, making it more prone to leaks and structural failure. The challenge is exacerbated in systems using metallic supports, as any wear or compromise in protective coatings exposes the support and pipe to aggressive corrosive attack. CUPS is often a hidden problem, only revealed when significant damage has already occurred, making it one of the leading causes of unexpected leaks and failures in piping systems.
One of the most effective ways to combat CUPS is the use of composite supports or the integration of non-metallic liners. These materials prevent moisture accumulation, eliminate metal-to-metal contact, and resist the corrosive environment, reducing the likelihood of CUPS-related leaks.
Challenges of Traditional Metallic Supports in Corrosive Environments
Limitations of Metallic Supports
- Susceptibility to Corrosion: Even with protective coatings, metallic supports can be easily compromised through scratches, impact damage, or coating degradation. Once the bare metal is exposed, corrosion accelerates rapidly, especially in environments with high moisture or chemical exposure.
- High Maintenance and Inspection Costs: To prevent failures, frequent inspections and maintenance are required for metallic supports. Re-coating and replacement of supports can be both costly and time-consuming, often leading to system downtime.
- Weight and Installation Complexity: Metallic supports are heavy, requiring specialized equipment for installation and making repairs in confined or elevated spaces more challenging. The increased labor and equipment costs add to the total lifecycle cost of metallic supports.
Consequences of Corroded Supports
- Structural Instability: Corroded supports compromise the entire piping system’s structural integrity. As supports degrade, pipes may sag or misalign, leading to increased stress on joints and other connection points.
- Increased Risk of Leaks: Corrosion at the pipe-support interface creates weak points in the pipe wall, increasing the likelihood of leaks. These leaks not only lead to environmental hazards but also cause downtime and increased maintenance costs.
- Environmental and Safety Hazards: Leaks in industrial systems can cause dangerous spills, fires, or contamination of surrounding areas. In chemical plants or refineries, even small leaks can escalate into severe safety incidents.
Composite Supports: The Corrosion-Resistant Solution
Corrosion Resistance
- No Galvanic Corrosion: Unlike metals, composites are non-conductive and therefore do not suffer from galvanic corrosion. This is particularly important when using RedLineIPS composite supports, as they prevent interaction between dissimilar metals in a corrosive electrolyte.
- Chemical Resistance: Composite supports like the RedLineIPS SmartPad System are resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and solvents, making them suitable for applications in chemical processing plants and refineries.
Lightweight and Easy to Install
- Reduced Installation Time: Lightweight composite materials reduce the need for heavy lifting equipment and allow for faster, simpler installation.
- Lower Transportation Costs: Because composite materials weigh significantly less than metals, transportation costs are lower, especially for offshore or remote locations.
High Strength and Durability
- Long Lifespan: The inherent durability of composite materials means fewer replacements, reducing the overall maintenance burden over the lifespan of the system.
- High Load-Bearing Capacity: Products like the RedLineIPS FRP Wear Pads are capable of handling heavy loads in demanding industrial environments while resisting wear and abrasion.
Low Thermal Conductivity
- Prevents Condensation: The low thermal conductivity of composites helps prevent the formation of condensation on the support, which could otherwise lead to corrosion under insulation.
- Improves Energy Efficiency: In temperature-sensitive applications, composite supports help maintain temperature stability, reducing energy losses.
The Role of Non-Metallic Liners in Corrosion Prevention
In applications where metallic supports are necessary, the use of non-metallic liners can make a significant difference in preventing corrosion. Liners act as a barrier between the metal and the pipe, eliminating metal-to-metal contact, which is a common cause of CUPS and other corrosion-related issues.
How Non-Metallic Liners Work
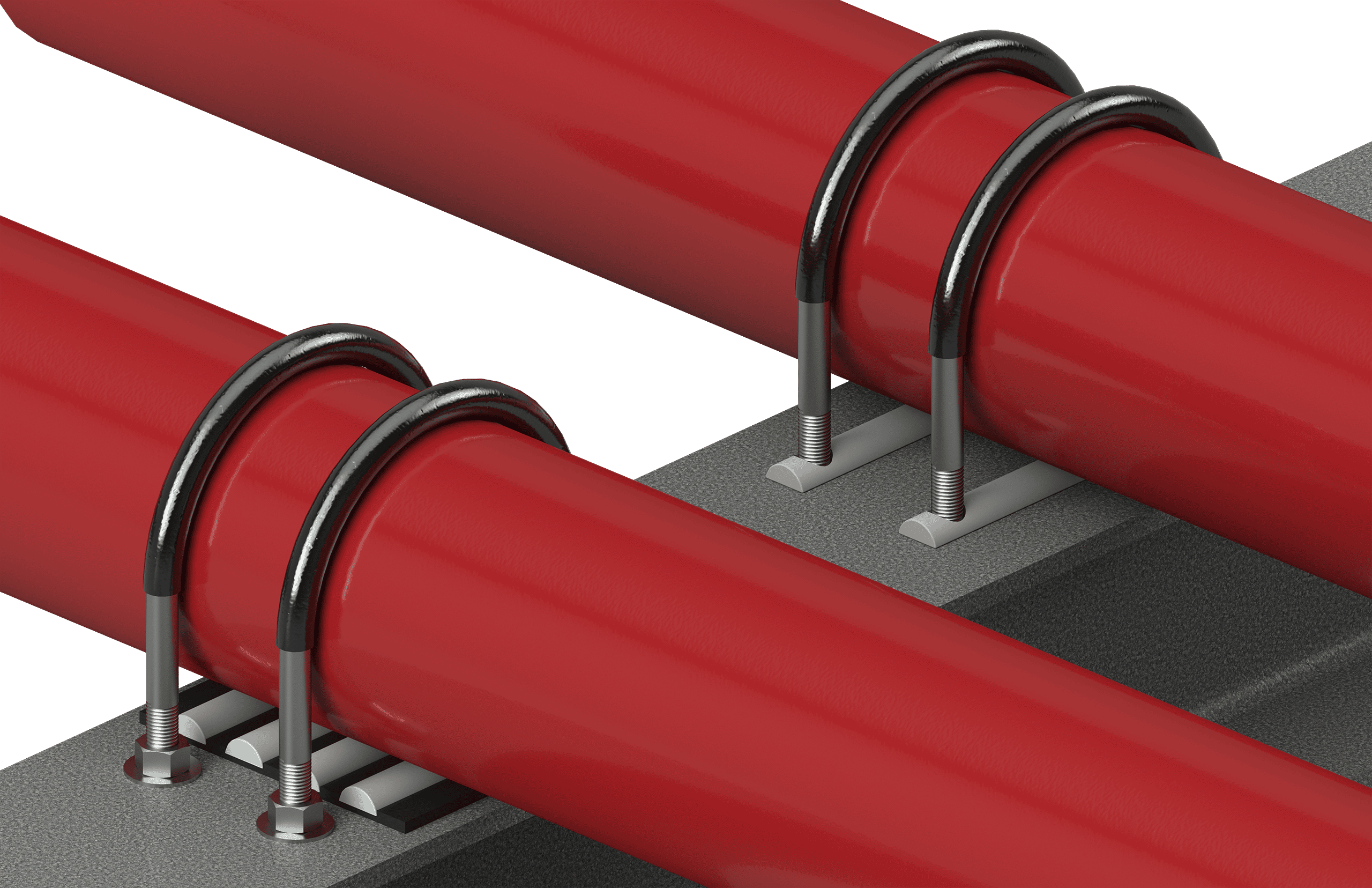
Non-metallic liners, like the RedLineIPS Clamp SmartInserts, are installed between the pipe and its support. These liners prevent direct contact between the metal surfaces, which is crucial in environments prone to galvanic corrosion.
- Isolation from Corrosive Elements: By eliminating metal-to-metal contact, non-metallic liners prevent the formation of crevices where moisture and corrosive chemicals can accumulate.
- Vibration and Impact Resistance: In addition to preventing corrosion, non-metallic liners absorb vibrations and protect the pipe from mechanical damage, further extending the system's lifespan.
Best Practices for Implementing Composite Supports and Non-Metallic Liners
Design Considerations
- Material Selection: Choose composite and liner materials that are compatible with the specific chemicals and environmental conditions of your system.
- Support Spacing: Properly space supports to prevent uneven load distribution, which can cause stress and potential failure.
Installation Guidelines
- Alignment: Ensure that supports are properly aligned to distribute the load evenly and avoid stress concentrations.
- Secure Attachment: Use appropriate fasteners and avoid over-tightening, which could damage the liner or pipe.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
- Visual Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to check for signs of wear or damage, particularly in areas where liners are used to prevent metal-to-metal contact.
- Cleaning: Periodic cleaning of supports and liners can remove chemical residues that could degrade performance over time.
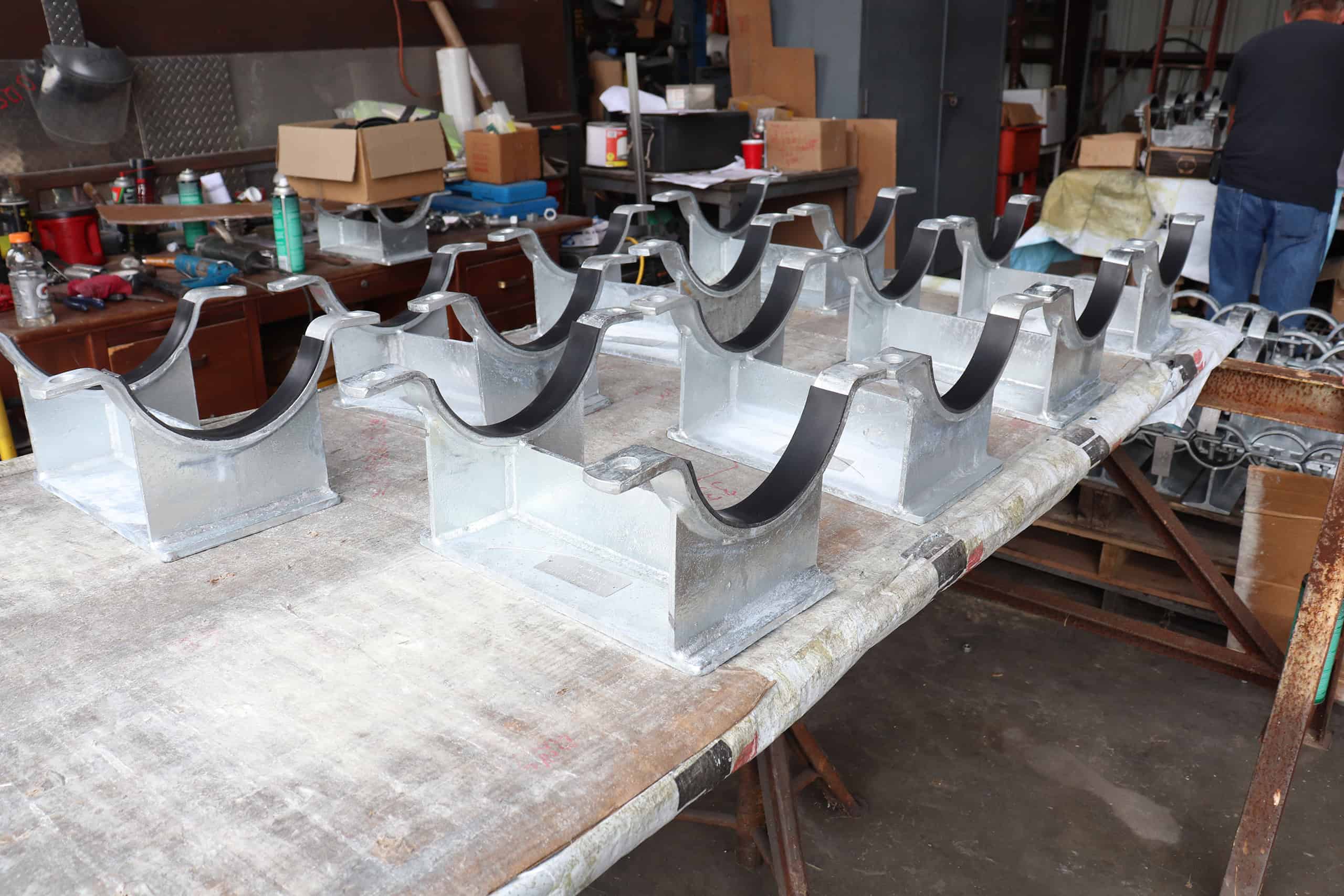
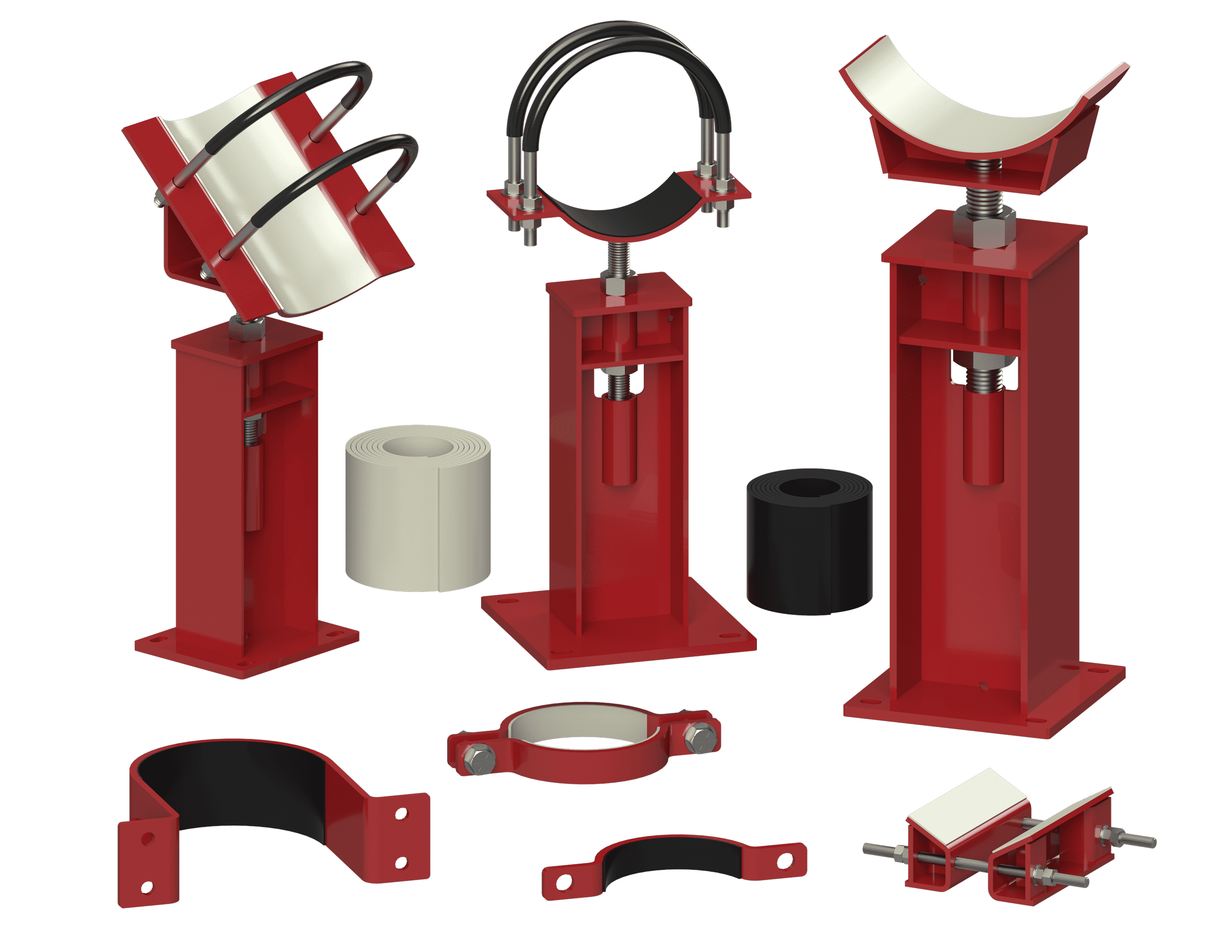
RedLineIPS Non-Metallic Products
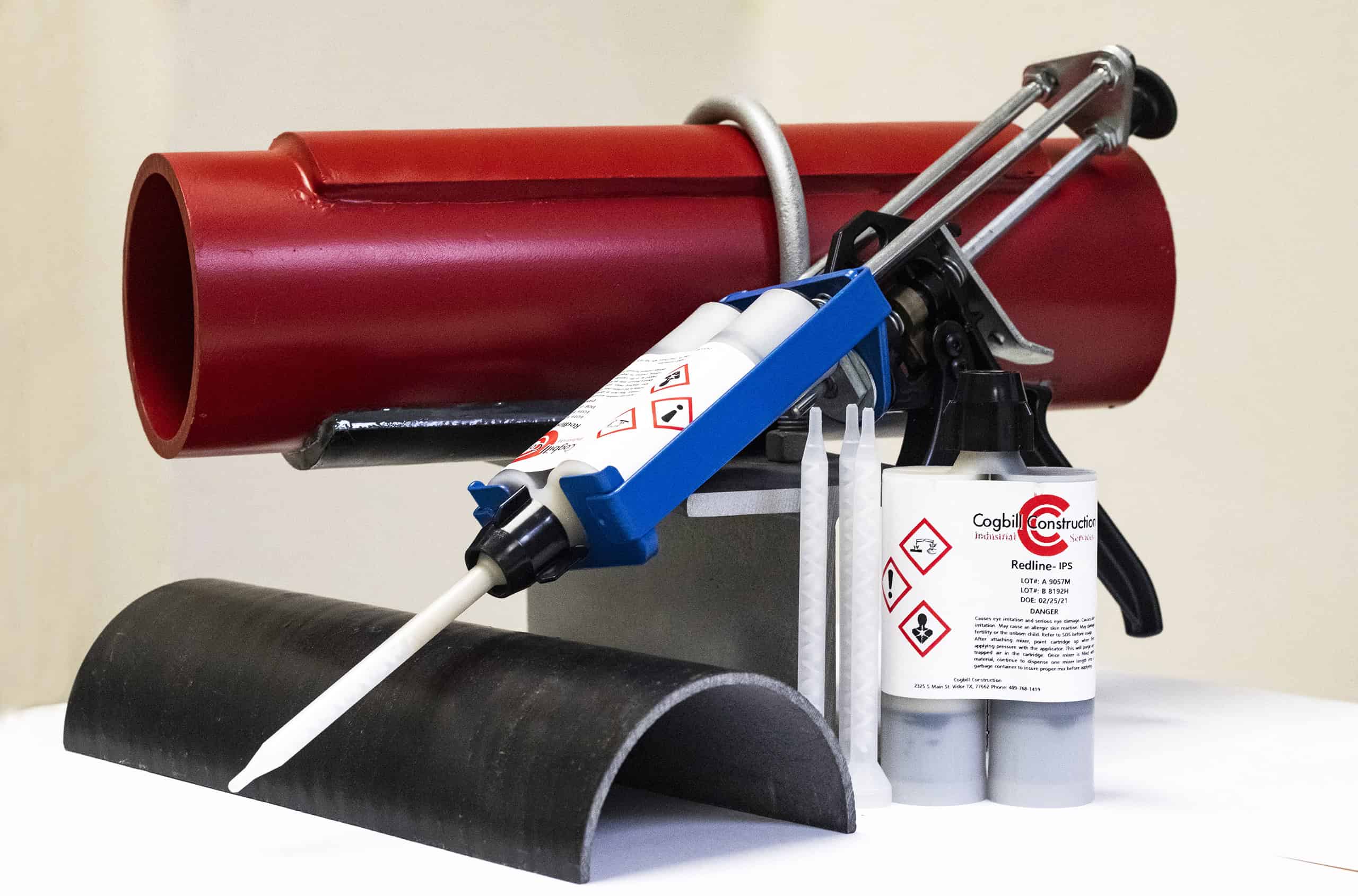
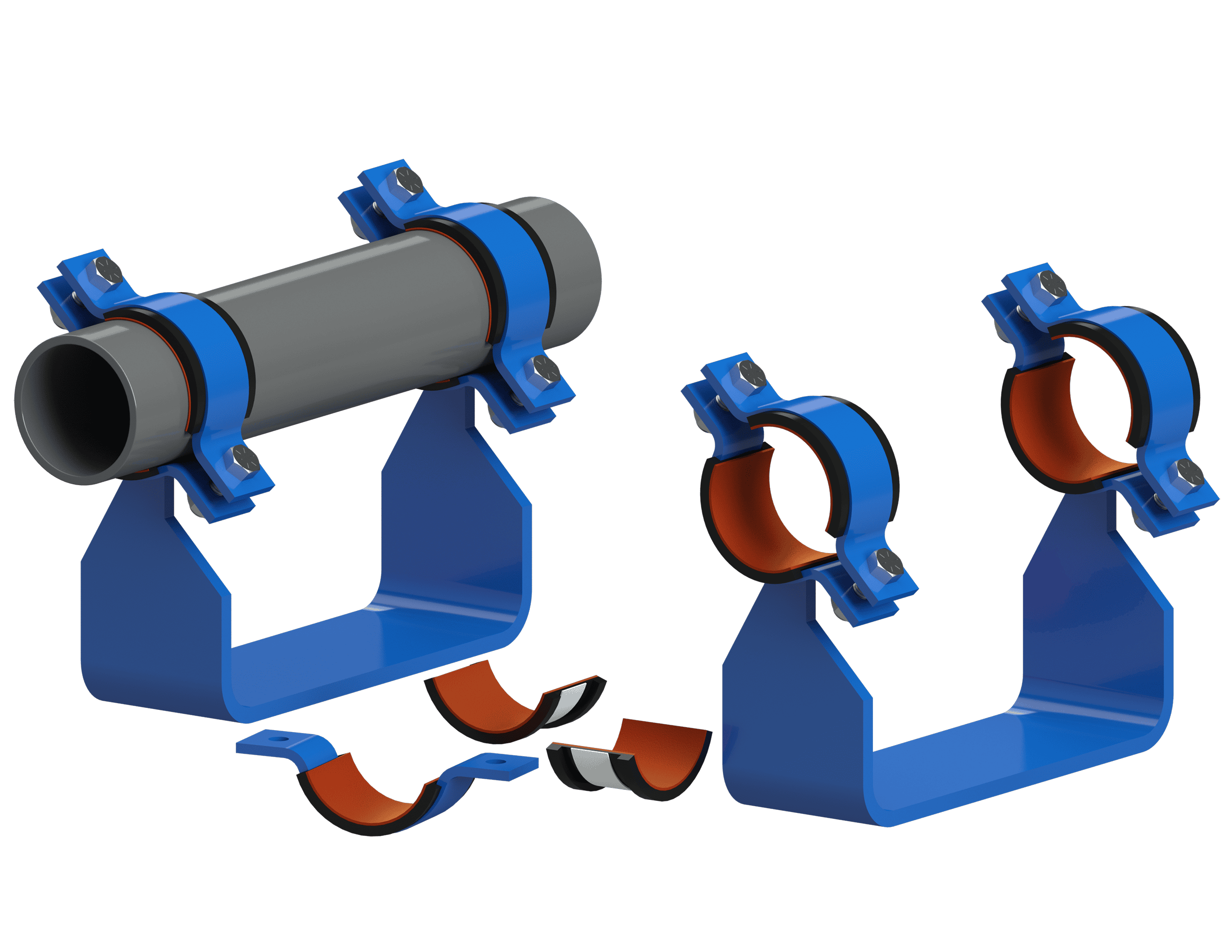
- SmartPad System: The SmartPad System from Cogbill, patent-pending, is a pioneering fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) Wear Pad System designed to protect above-ground piping systems from external corrosion at the pipe support points. The SmartPads neither require epoxy nor welding for installation, enabling swift installation, removal, and reinstallation in minutes. This drastically reduces installation, corrosion inspection, and maintenance costs, hence significantly reducing total cost of ownership.
- FRP Wear Pads and Flat Pads: FRP wear pads and flat pads are durable, corrosion-resistant components used to protect above-ground piping from external corrosion at support points (CUPS). They prevent direct metal-to-metal contact, protect the pipe’s protective paint coating, and prevent crevice corrosion, thus extending the lifespan of the piping system.
- RIBS System: The RIBS system combines half-round thermoplastic rods with specialized FRP flat pads to elevate pipes above their metallic supports, preventing external corrosion at the support points. It facilitates easy installation, eliminates the need for drilling, and allows for rapid inspection and maintenance, making it a robust solution for industrial piping systems.
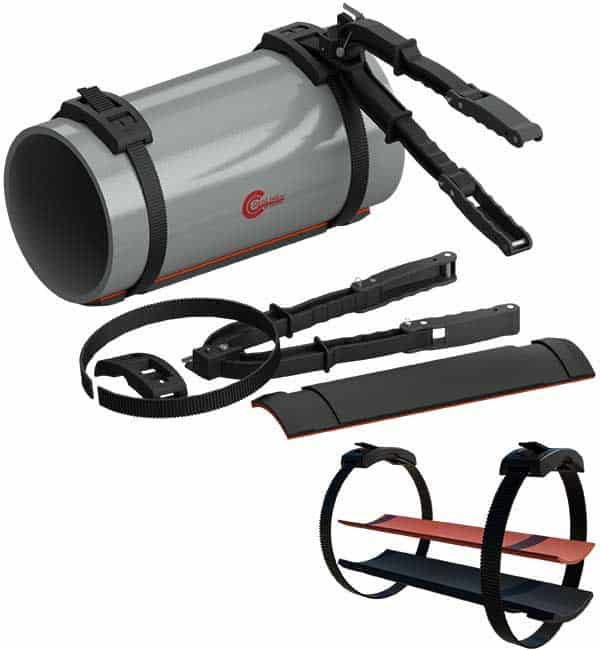
- Clamp SmartInserts: Cogbill’s RedLineIPS Clamp SmartInserts are an innovative, non-metallic pipe external corrosion-protection system that can be fitted into non-welded clamped pipe supports, such as clamped-on pipe shoes and similar components. When installed, this non-metallic system prevents water from ever invading the support/pipe interface, thus protecting the pipes from galvanic corrosion affecting the external part of the pipe at the pipe support points.
- Isolation Liners: Isolation liners are protective barriers that fit onto various pipe supports to shield industrial piping systems from mechanical wear, corrosion, vibration, and noise, thus enhancing longevity and maintaining system integrity. These liners are tailored to fit different support structures and pipe dimensions. They include a wide variety of materials such as PTFE, Fabreeka, PVC, Cotton Duck Pads, and many more.
In short, corrosive environments present unique challenges to industrial piping systems, with traditional metallic supports often falling short due to their susceptibility to corrosion. Composite supports, such as those from RedLineIPS, provide an effective, long-lasting solution that can significantly reduce maintenance costs, enhance safety, and extend the lifespan of the system. By integrating non-metallic liners and composite supports, industries can effectively prevent leaks, mitigate corrosion, and ensure the reliability of their piping systems.
For more information on how RedLineIPS composite supports and non-metallic liners can help you protect your piping systems from corrosion and prevent leaks, visit RedLineIPS Non-Metallic Products.