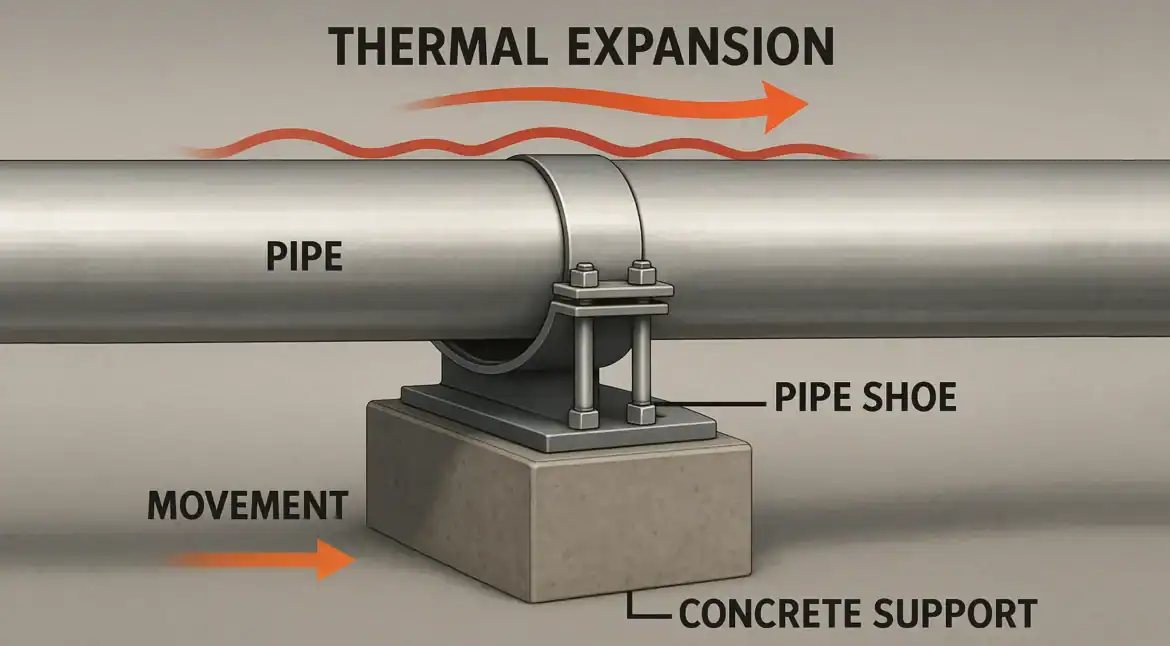
In industrial piping systems, thermal expansion is a critical factor that must be carefully managed. Temperature fluctuations cause pipes to expand and contract, creating movement that can lead to stress, misalignment, or even structural failure. Without effective management of this movement, pipes, their supports, and the surrounding infrastructure can be damaged over time.
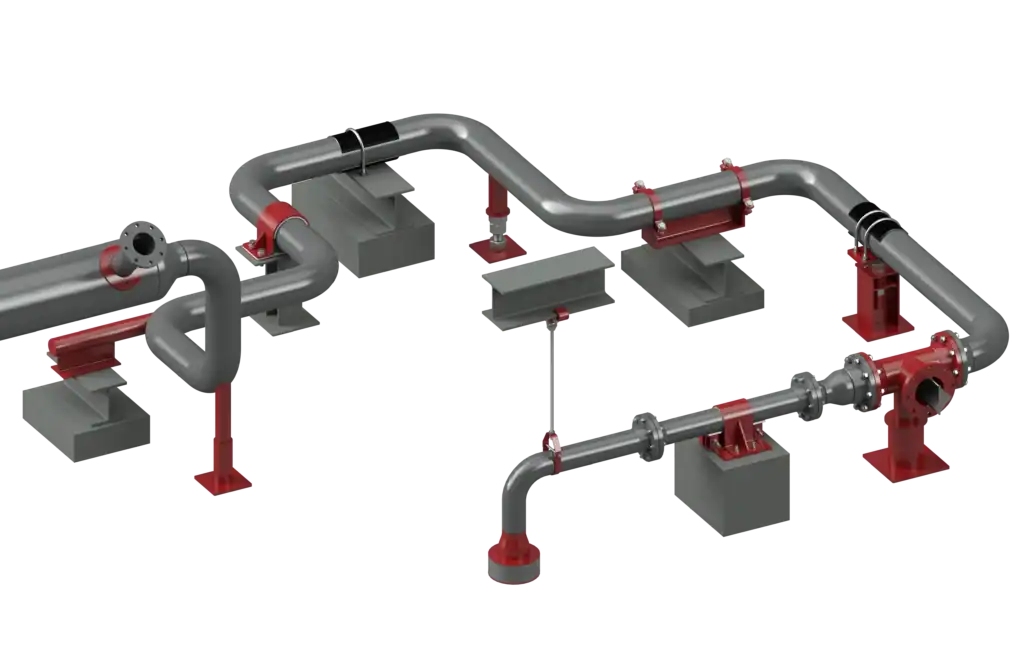
The key to addressing thermal expansion lies in using specialized pipe supports that allow for controlled movement while preventing unwanted stress. At RedLineIPS, we offer a comprehensive range of adjustable and non-adjustable supports, as well as pipe shoes equipped with features like clamps, slide plates, isolation liners and guide supports, to ensure that industrial piping systems can safely expand and contract without compromising their integrity.
What is Thermal Expansion?
Thermal expansion is the phenomenon where a material increases in length as it heats up and contracts as it cools. In piping systems, this means that when the temperature rises, pipes will expand, and when the temperature drops, pipes will contract. This expansion and contraction can create significant forces, leading to mechanical stress if not properly managed. The degree of thermal expansion depends on:
- Material Type: Different materials expand at different rates. For example, carbon steel has a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of approximately 0.0000065 in/in/°F, meaning it expands by 0.0000065 inches per inch of length for each degree of temperature change. Stainless steel expands slightly more.
- Temperature Range: The greater the temperature variation, the more expansion or contraction occurs.
- Pipe Length: Longer pipes experience more significant total expansion. For example, a 100-foot steel pipe could expand nearly 1 inch for every 150°F temperature increase.
Thermal Expansion Effects on Piping Systems and Supports
Uncontrolled thermal expansion in industrial piping can result in several issues, among them are:
- Pipe Stress: As pipes expand and contract, they exert significant forces on connected equipment, fittings, and supports. If this movement is not managed, it can lead to material fatigue, stress fractures, or even rupture.
- Misalignment: Expansion can cause pipes to shift from their original positions, leading to misalignment, which affects the flow of fluids and can lead to leaks or damage to connections.
- Buckling and Warping: When the movement of a pipe is restricted, thermal expansion can lead to buckling or warping, compromising the structural integrity of the system.

- Impact on Pipe Racks: Pipe racks, which support long runs of piping, must also accommodate thermal movement. If the supports on these racks do not allow for sufficient movement, stress will be transferred to the rack itself, potentially causing deformation or structural failure.
- CUPs Corrosion: When pipes expand and slide across metal supports without protective barriers, the friction between the pipe and the support surface can wear through paint or coating systems. This exposes bare metal to moisture and air, leading to localized corrosion and the onset of corrosion under pipe supports (CUPS). This damage often begins invisibly and worsens over time, especially in coastal, humid, or process-intense environments.
Best Practices for Managing Thermal Expansion
To effectively address thermal expansion in piping systems, it is essential to implement a combination of engineered supports and expansion management systems. Below are three best practices that help mitigate the impact of thermal expansion in industrial piping.
- Metallic Supports with Clamps and Liners: Adjustable supports, non-adjustable supports, hold-down clamps, and pipe shoes are all designed to handle the controlled movement of pipes due to thermal expansion. One key method involves incorporating isolation liners within the clamping mechanisms or saddles of these supports. The liners help absorb the forces generated by expansion, ensuring the pipes can move axially without metal-to-metal contact.
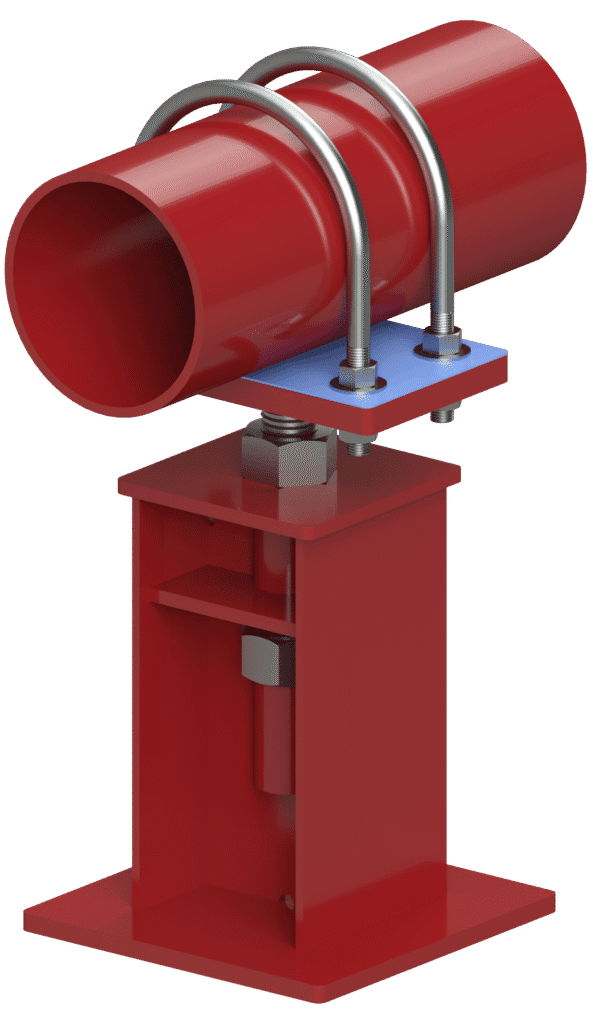
How Isolation Liners Work in Clamping Mechanisms:
The isolation liners are typically placed between the pipe and the support clamp or saddle, forming a protective layer that allows the pipe to slide along its axis as it expands and contracts. This prevents the pipe from binding or causing damage to the support structure. Isolation liners also absorb vibration and reduce noise transmission, contributing to both the longevity of the support and the safety of the piping system.
Installation of Isolation Liners:
- Pre-fitted Liners: Many supports come pre-fitted with liners that are specifically designed for the pipe diameter. These liners are typically secured using high-temperature adhesives or mechanical fastening
- Custom Liners: For unique applications, custom isolation liners are often required. These can be tailored in terms of thickness, material type, and flexibility to meet the specific expansion characteristics of the piping system. Contact us if you would like more details.
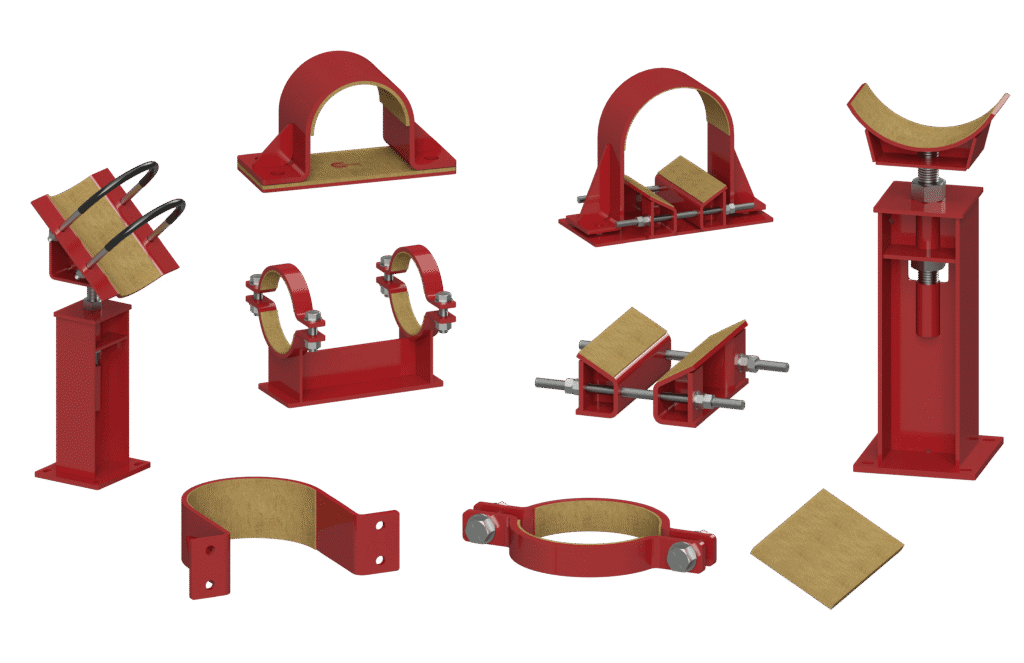
Suitable Isolation Liner Materials:
Isolation liners come in various materials suited to different environments and operational demands. Material selection must consider operating temperature, chemical exposure, compressive strength, vibration frequency, and long-term durability. Below are commonly used liner materials, each selected for specific environmental and mechanical demands:
- Neoprene (Polychloroprene): Neoprene is a synthetic elastomer with excellent resistance to a broad spectrum of chemicals, including oils, greases, and mild acids. It has a working temperature range typically between -40°F to 225°F (-40°C to 107°C) and offers a good balance of flexibility and resilience. With a Shore A hardness ranging from 40 to 70, Neoprene liners are ideal for process plants handling lubricants, fuels, or hydraulic fluids. Their moderate compressive strength (~1000 psi) makes them suitable for medium-load pipe support applications. Applications: Chemical plants, refineries, general-purpose industrial systems exposed to oils and mild solvents.
- Nitrile Rubber (Buna-N / NBR): Nitrile rubber is known for its outstanding oil and fuel resistance, making it particularly well-suited for petrochemical and upstream oil and gas environments. NBR has a typical service temperature range of -40°F to 250°F (-40°C to 121°C) and offers excellent compression set resistance. It can handle repeated expansion cycles without significant loss in elasticity. NBR also performs well in systems containing aliphatic hydrocarbons and certain hydraulic fluids. Shore hardness typically falls between 60–70 A, with compressive strengths up to 1500 psi. Applications: Oil and gas pipelines, compressor supports, terminals, and process units handling petroleum-based products.
- EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): EPDM rubber is a non-polar elastomer with excellent resistance to water, steam, ozone, and UV radiation. It performs well in outdoor and high-humidity environments, including cooling towers and utility corridors. EPDM can withstand temperatures from -50°F to 300°F (-45°C to 149°C), making it suitable for cyclic thermal environments. Though it lacks oil resistance, its weathering and dielectric properties make it a good choice for systems where water ingress is a concern. Its relatively high elongation before break (~300%) helps absorb pipe motion. Applications: Power plants, chiller lines, cooling towers, water treatment, pulp and paper facilities.
- Cotton Duck Pads (Rubber-Impregnated Fabric): Cotton duck pads consist of multiple layers of woven cotton fabric impregnated with nitrile or neoprene rubber. This composite structure provides directional strength and excellent vibration-dampening characteristics due to the interlocking fabric weave. These pads typically exhibit Shore D hardness of 45–55 and compressive strengths exceeding 2000 psi, with temperature capabilities up to 225°F (107°C). Their ability to absorb shock and dissipate vibrational energy makes them ideal for high-cycle environments. Applications: Facilities with high-frequency rotating equipment such as pumps, compressors, or reciprocating machinery. Used extensively in gas plants and industrial manufacturing lines.
- Fabreeka Pads (Molded Fabric-Reinforced Elastomers): Fabreeka pads are engineered vibration isolation pads made from layers of cotton duck or similar fabric molded into a nitrile rubber matrix. They offer extremely high compressive strength (up to 10,000 psi), excellent rebound recovery, and consistent load deflection characteristics. These pads are typically used where high static and dynamic loads are present. Fabreeka materials can also accommodate structural misalignment due to their ability to deform while maintaining load-bearing capacity. Applications: Heavy industrial equipment, structural steel supports, high-load pipe supports, bridge bearings, and pump bases.
When selecting an isolation liner material, engineers must account for:
- Operating Temperature Range
- Compressive Load Capacity (static and dynamic)
- Chemical Compatibility (oils, solvents, acids, steam, etc.)
- Coefficient of Friction (impacts pipe sliding performance)
- Aging Resistance (UV, ozone, thermal cycling)
- Installation Method (bonded vs. clamped)
A proper match between liner material and service conditions ensures not only improved performance during thermal expansion/contraction cycles but also prolonged system life and reduced maintenance.
For more detailed specifications and applications of these materials, visit the RedLineIPS Isolation Liners page or contact us any time.
- Metallic Supports with Slide Plates: Another effective method of managing thermal expansion in piping systems involves the use of slide plates at the base of metallic supports, such as adjustable supports, non-adjustable supports, hold-down clamps, and pipe shoes. Slide plates enable the horizontal movement of pipes by reducing friction between the pipe and the support, allowing for controlled expansion and contraction along the pipe’s axis.
How Slide Plates Work in Metallic Supports:
Slide plates are typically installed on the base plate of the support, providing a low-friction interface between the pipe and the support structure. As the pipe expands due to heat, the slide plate ensures smooth, controlled movement, reducing the chances of stress concentration or pipe buckling.
The coefficient of friction plays a critical role in slide plate performance. PTFE (Teflon) slide plates typically offer the lowest friction range—between 0.05 to 0.10—making them ideal for reducing drag during pipe movement. When paired with polished stainless steel, this value can drop as low as 0.04, allowing exceptionally smooth sliding under load. Graphite plates, commonly used in high-temperature applications, provide a slightly higher friction range of 0.10 to 0.15, but offer excellent thermal resistance. In contrast, standard lubricated steel-on-steel slide plates may have coefficients as high as 0.20, requiring more force to accommodate movement and potentially leading to increased wear. Selecting the right slide plate material based on load, temperature, and movement expectations is key to minimizing friction-related coating damage and long-term corrosion.

Installation of Slide Plates:
- Bolted or Welded Installation: Slide plates are either bolted or welded onto the support’s base plate. Bolted systems allow for easy replacement of the slide plate when worn, while welded systems offer a more permanent solution for systems with high vibration or continuous movement.
- Alignment and Load Distribution: Proper alignment is critical to ensure that the slide plate works in harmony with the pipe’s expansion direction. Misalignment can result in excessive friction, causing wear and eventual failure of the support. Additionally, the size of the slide plate must be carefully engineered to distribute the thermal load evenly, particularly in systems with long piping runs.
Types of Slide Plate Materials:
- PTFE (Teflon) Slide Plates: Known for its low-friction properties, PTFE slide plates are excellent for general applications and can withstand temperatures up to 500°F.
- Graphite Slide Plates: Suitable for high-temperature applications, graphite plates can handle extreme temperatures beyond 1000°F while still providing a low-friction surface.
- Stainless Steel Slide Plates: Often used in corrosive environments, stainless steel slide plates provide durability, strength, and resistance to wear and corrosion.
Research and industry experience show that frictional contact between bare pipe and steel supports can generate coefficients of friction exceeding 0.5, particularly under high-load or high-temperature conditions. This repetitive sliding causes protective coatings to degrade or shear off, exposing the pipe to corrosive environments. By using slide plates or non-metallic wear pads with ultra-low coefficients of friction—such as PTFE (as low as 0.1)—you can significantly reduce this damage. This not only protects the pipe coating but also helps prevent corrosion under pipe supports (CUPS), a leading cause of long-term system degradation.
By employing slide plates, metallic supports allow the pipe to move freely as it expands or contracts, ensuring the piping system remains stable and protected from thermal stress.
- Other Solutions for Managing Thermal Expansion: In addition to using metallic supports with isolation liners or slide plates, certain systems may require additional expansion management devices to accommodate extreme movement or complex configurations. These solutions are often employed in conjunction with traditional pipe supports.
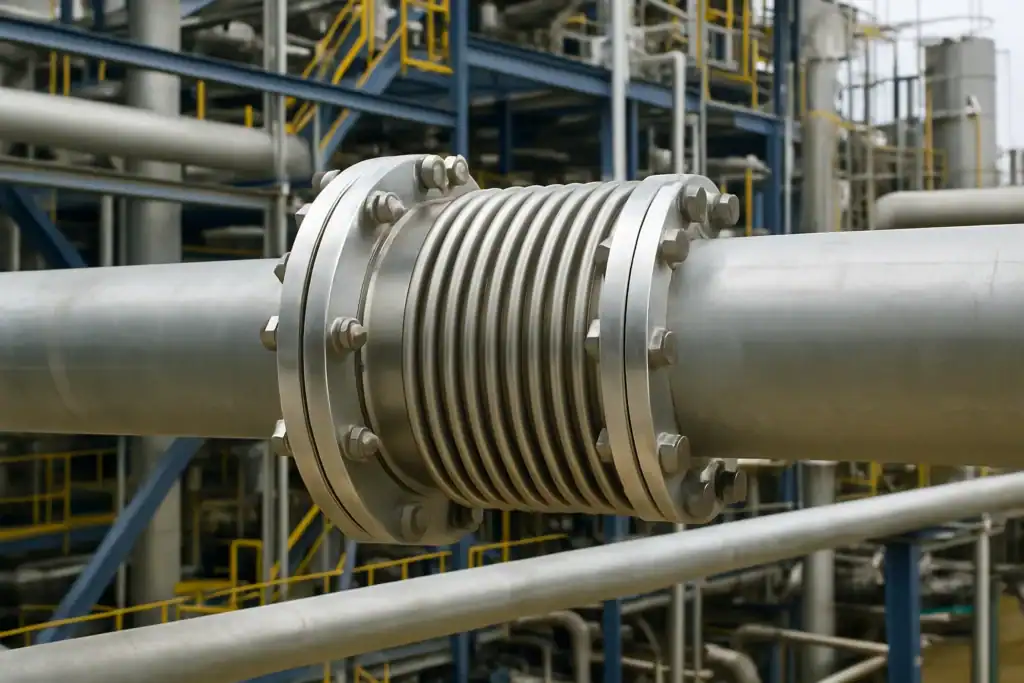
a) Expansion Joints
Expansion joints are flexible connectors installed between sections of pipe to absorb axial, lateral, or angular movement caused by thermal expansion. These joints are used when the movement exceeds what a standard support system can accommodate. They are typically made of materials such as metal bellows or rubber, depending on system requirements.
- Metal Bellows Expansion Joints: These are designed to absorb large amounts of movement in high-temperature applications. Metal bellows expansion joints can handle significant axial expansion while maintaining a pressure-tight seal.
- Rubber Expansion Joints: Common in lower-temperature systems, rubber expansion joints offer excellent flexibility and vibration dampening, making them ideal for applications where both movement and vibration control are required.
b) Expansion Loops and Bends
Another method for absorbing the movement caused by thermal expansion is the use of expansion loops or bends in the piping system. Expansion loops are carefully designed sections of piping that create a flexible segment, allowing for natural movement without stressing the system.
Expansion loops must be engineered to account for the length of the pipe and the amount of expected movement. They are typically used in long, straight piping runs where axial movement is significant.
c) Flexible Connectors
Flexible connectors are another option for managing thermal expansion. These components are often installed between piping and equipment (e.g., pumps or compressors) to absorb movement and reduce stress at connection points.
d) Braided Metal Hoses
These flexible connectors provide lateral flexibility and absorb movement caused by thermal expansion. They are ideal for systems where fluid flow or machinery movement creates additional stress on the pipe.
Design Considerations for Thermal Expansion Management
When designing a piping system to accommodate thermal expansion, several critical factors must be considered to ensure that the system remains functional and free from stress.
- Material Selection: Selecting the right material for both the pipes and the supports is crucial. Stainless steel and carbon steel are commonly chosen for industrial piping systems because of their predictable expansion properties. The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) must be carefully matched with the intended temperature range of the system.
- Support Spacing: Proper support spacing is essential for managing both thermal expansion and the weight of the pipes. Incorrect spacing can cause sagging, stress, or misalignment. The correct distance between supports should be calculated based on the pipe material, expected temperature changes, and the weight of the piping system.
- Expansion Loops and Bends: Beyond immediate mechanical performance, thermal expansion solutions should be evaluated from a lifecycle cost perspective. Selecting higher-quality pipe supports with integrated liners or corrosion-resistant materials may have higher up-front costs but can prevent shutdowns, pipe replacements, or coating failures that result in significant downtime and maintenance expenses. The return on investment for these components becomes clear over a 5–10 year operating period.
- Lifecycle Cost Considerations: In long piping runs, expansion loops or bends are often introduced to absorb the movement caused by thermal expansion. These loops create flexible sections of the piping system that allow the pipe to expand naturally without putting excess stress on the pipe or its supports.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper installation and ongoing maintenance are critical for ensuring that the thermal expansion management solutions remain effective.
Installation Guidelines
- Alignment: All supports and clamps must be properly aligned to allow for expected movement. Misalignment can lead to stress fractures or buckling.
- Insulation: In cryogenic and high-temperature systems, proper insulation must be used to prevent heat transfer and to minimize the effects of thermal expansion.
Maintenance Tips
- Regular Inspections: Conduct periodic inspections to check for signs of wear, misalignment, or corrosion on the supports, slide plates, and liners.
- Lubrication: In cryogenic and high-temperature systems, proper insulation must be used to prevent heat transfer and to minimize the effects of thermal expansion.
- Friction Monitoring: For systems experiencing frequent thermal cycling, monitor the areas of contact between pipe and support. Signs of coating wear or paint dust accumulation can be early indicators of friction-induced damage, and may suggest a need for wear pad retrofitting or liner upgrades.
- Adjustment: Over time, pipe supports may need adjustment to maintain their effectiveness as the system experiences wear or shifts.
Effectively managing thermal expansion in industrial piping systems is essential for long-term system reliability, safety, and corrosion prevention. The use of engineered pipe supports, liners, and expansion components like slide plates and joints plays a vital role in ensuring that thermal movement is accommodated without compromising structural integrity or coating performance.
At RedLineIPS, we specialize in a wide range of pipe support solutions engineered to handle thermal expansion, corrosion under pipe supports (CUPS), and vibration-related fatigue. Our product lines include adjustable pipe supports, clamp systems, slide plate-equipped supports, and isolation liners, all designed to enhance system performance across industrial, petrochemical, and offshore environments.
To learn more about how RedLineIPS products can help you mitigate the effects of thermal expansion and improve the longevity of your piping systems, contact us at (409) 768-1419 or email Sales@RedLineIPS.com. You can also explore our full catalog of solutions by visiting www.RedLineIPS.com.