Industrial piping systems are the backbone of many industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and water treatment. These systems are responsible for transporting fluids, gases, and other materials essential to the operation of industrial processes. However, the effectiveness and safety of these systems depend not only on the quality of the pipes themselves but also on the structural components that support them. Pipe supports play a critical role in ensuring the stability, safety, and longevity of industrial piping systems and pipelines. This comprehensive blog post explores why pipe supports are needed, the roles they play, how they function, and their importance in various industrial settings.
Why Pipe Supports Are Necessary?
Pipes in industrial systems are subjected to a wide range of stresses and forces that can lead to significant issues if not properly managed. These forces include the weight of the pipes and the materials they carry, thermal expansion and contraction, vibrations, and external loads. Without adequate support, these forces can cause pipes to sag, bend, or even break, leading to leaks, system failures, and costly repairs.
Key Reasons for Pipe Supports:
- Weight Management: Pipes can be heavy, especially when they are filled with fluids or gases. The weight of these materials can cause pipes to sag or deform over time. Pipe supports are designed to bear the weight of the pipes and their contents, preventing sagging and ensuring that the pipes remain in their intended positions.
- Thermal Expansion and Contraction: Industrial processes often involve the transport of materials at varying temperatures. As pipes heat up or cool down, they expand or contract. This thermal movement can put significant stress on the piping system, leading to misalignment, leaks, or even ruptures. Pipe supports help manage this thermal expansion and contraction by allowing the pipes to move as needed without causing damage, for example via the use of slide plates.
- Vibration Control: In many industrial settings, piping systems are subject to vibrations from machinery, pumps, or fluid flow. These vibrations can cause pipes to move, leading to fatigue, wear, and eventual failure. Pipe supports are designed to absorb and dampen these vibrations, especially with the use of isolation liners, protecting the integrity of the piping system.
- Load Distribution: Pipes are often subjected to external loads, such as wind, seismic activity, or the weight of attached equipment. Pipe supports distribute these loads evenly across the piping system, preventing localized stress points that could lead to failure.
- Safety and Compliance: Properly supported pipes are essential for maintaining a safe working environment. Inadequate pipe support can lead to accidents, such as pipe collapses or leaks, which can pose serious safety risks to workers and the surrounding environment. Moreover, many industrial regulations and standards require the use of appropriate pipe supports to ensure compliance with safety and engineering codes.
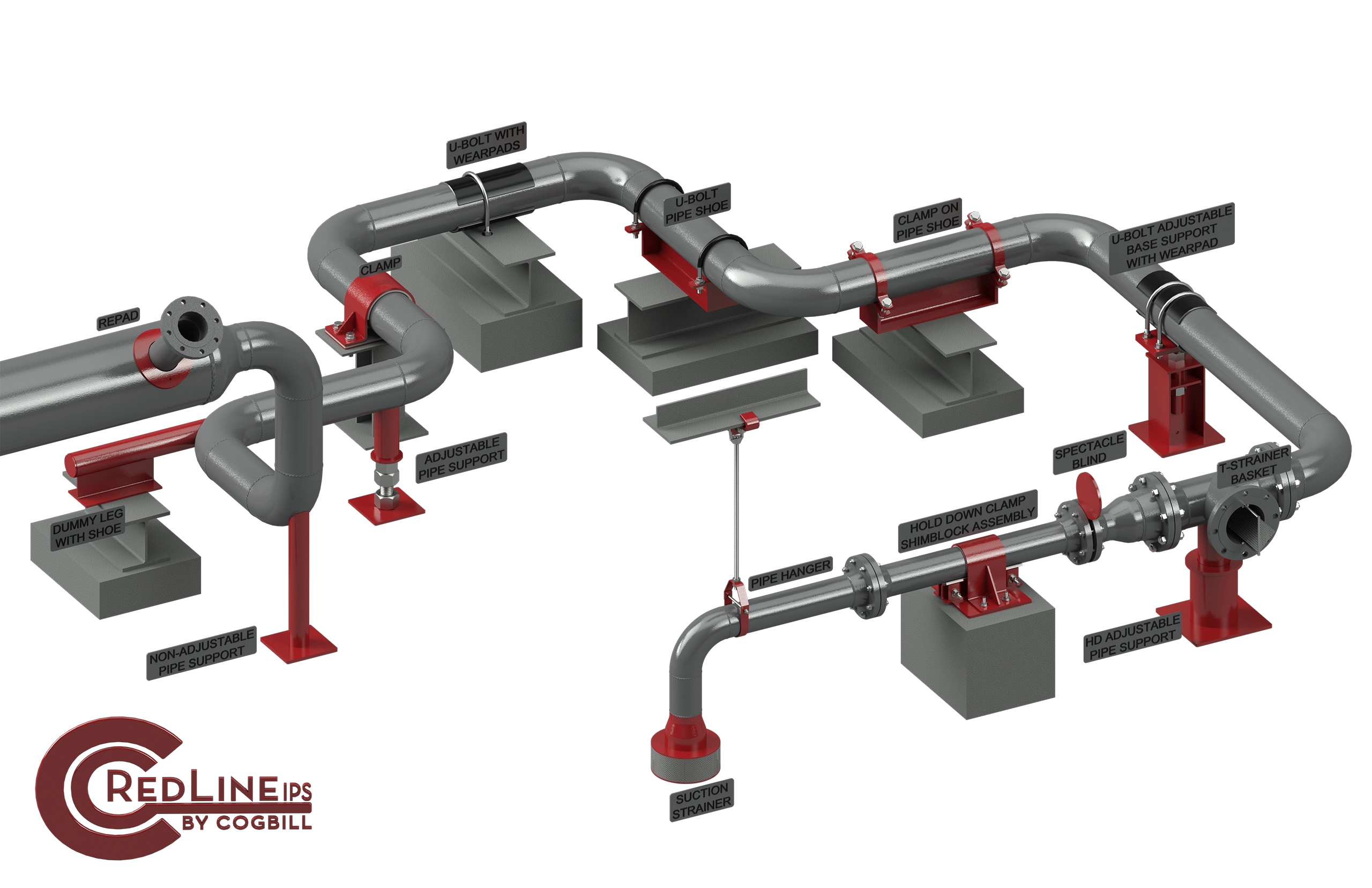
The Role of Pipe Supports in Piping Systems
Pipe supports are critical components that perform several vital functions in industrial piping systems. Their primary roles include maintaining the alignment of the pipes, supporting the weight of the pipes and their contents, managing thermal expansion and contraction, and protecting the pipes from external forces.
- Maintaining Pipe Alignment: One of the most important roles of pipe supports is to maintain the proper alignment of the piping system. Pipes need to be aligned correctly to ensure that the flow of materials is smooth and uninterrupted. Misaligned pipes can cause flow restrictions, increased pressure drop, and even blockages, leading to reduced system efficiency and potential damage to equipment. Pipe supports, especially adjustable pipe supports, keep the pipes in their intended positions, ensuring that they are properly aligned throughout the system. This is particularly important in complex piping networks, where misalignment in one section can have a cascading effect on the entire system.
- Supporting the Weight of Pipes and Contents: Pipes, especially those carrying fluids or gases, can be extremely heavy. The weight of the pipes themselves, combined with the weight of the materials they transport, can exert significant downward force. If this weight is not properly supported, it can cause the pipes to sag, bend, or even collapse, leading to leaks and system failures.
Pipe supports are designed to bear the weight of the pipes and their contents, distributing the load evenly across the system. This prevents sagging and deformation, ensuring that the pipes remain in their intended positions and function as designed.
- Managing Thermal Expansion and Contraction: Thermal expansion and contraction are natural consequences of temperature changes in industrial piping systems. As the temperature of the material inside the pipe fluctuates, the pipe itself will expand or contract. This movement can cause significant stress on the piping system, leading to misalignment, leaks, or even rupture if not properly managed.
Pipe supports play a crucial role in accommodating thermal expansion and contraction. Some supports, known as sliding or roller supports, such as pipe hangers and pipe clamps, allow the pipe to move longitudinally as it expands or contracts, without causing damage to the pipe or the support structure. This ensures that the piping system can handle temperature changes without compromising its integrity.
- Absorbing Vibrations and Shocks: Vibrations are a common occurrence in industrial piping systems, especially in systems that involve pumps, compressors, or turbulent fluid flow. These vibrations can cause pipes to move, leading to fatigue, wear, and eventual failure. In some cases, vibrations can even cause pipes to become dislodged from their supports, creating serious safety hazards.
Pipe supports are designed to absorb and dampen vibrations, reducing the risk of damage to the pipes and the surrounding infrastructure. Vibration-damping supports are often equipped with elastomeric or other resilient materials that cushion the pipe and minimize the effects of vibrations and shocks.
- Protecting Against External Loads: In addition to internal forces, pipes are often subjected to external loads, such as wind, seismic activity, or the weight of attached equipment like valves or sensors. These external loads can create stress points in the piping system, leading to bending, buckling, or even catastrophic failure.
Pipe supports help distribute these external loads evenly across the piping system, preventing localized stress concentrations. In seismic zones, for example, special seismic supports are used to anchor pipes securely and protect them from the forces generated during an earthquake.
How Pipe Supports Function
Pipe supports function by providing a stable foundation for pipes and distributing the forces acting on the piping system. They come in various designs, each suited to specific applications and load conditions. The choice of pipe support depends on factors such as the type of load, the temperature of the materials being transported, and the environmental conditions.
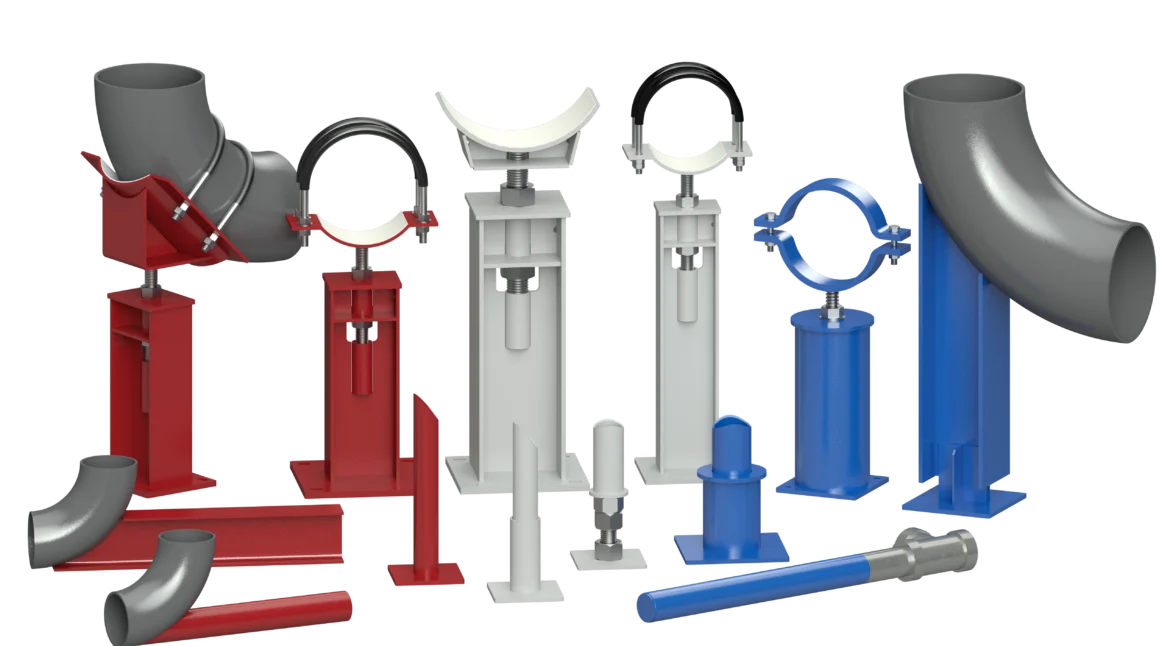
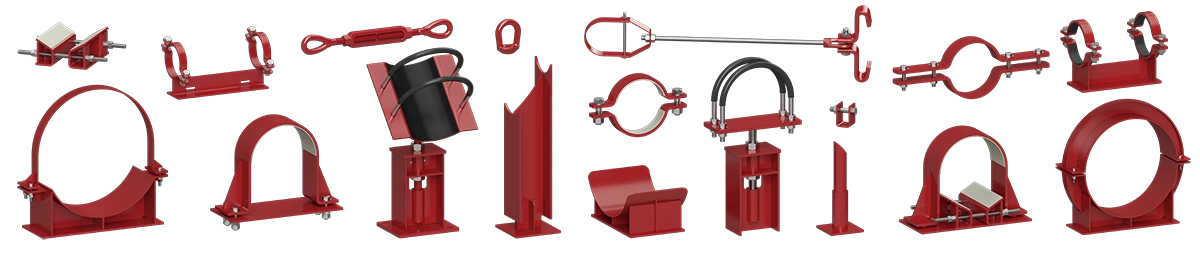
Types of Pipe Supports
There are several types of pipe supports, each designed to perform specific functions within an industrial piping system. Some of the most common types include:
- Hangers: Hangers are used to suspend pipes from above, providing vertical support. They are commonly used in applications where space is limited, such as in ceilings or tight corridors. Hangers can be adjustable or fixed, depending on the needs of the system.
- Saddles: Saddle supports cradle the pipe from below, providing support along its length. These supports are often used in horizontal piping systems and are designed to distribute the weight of the pipe and its contents evenly.
- Roller Supports: Roller supports allow pipes to move longitudinally, accommodating thermal expansion and contraction. These supports are often used in high-temperature systems where significant thermal movement is expected.
- Spring Supports: Spring supports are designed to absorb vertical movements, such as those caused by thermal expansion or vibration. They are often used in systems where the pipe needs to be able to move vertically without creating stress on the support structure.
- Anchors: Anchors are fixed supports that prevent any movement of the pipe. They are used to secure pipes at specific points, preventing them from shifting due to thermal expansion, vibration, or external loads.
Ensure your piping systems are supported by RedLineIPS, a brand committed to quality and punctual delivery. From pipe supports to custom industrial solutions, our team guarantees precision and reliability with every project. Contact us at Sales@RedLineIPS.com or call (409) 768-1419 to discuss your needs. RedLineIPS—delivering excellence on time, every time.